Monitoring & Observability
This guide covers monitoring Milvaion in production, including health checks, metrics, logging, and alerting.
Health Checks
API Health Endpoints
| Endpoint | Purpose | Use For |
|---|---|---|
/health/live | Is the process running? | Kubernetes liveness probe |
/health/ready | Are dependencies healthy? | Kubernetes readiness probe |
/health | Full health with details | Debugging, dashboards |
Liveness Check
curl http://localhost:5000/api/v1/healthcheck/live
Response:
{
"status": "Healthy",
"timestamp": "2026-01-14T17:55:12.5466734Z",
"uptime": "16.05:34:46.9359664"
}
Readiness Check
curl http://localhost:5000/api/v1/healthcheck/ready
Response:
{
"status": "Healthy",
"duration": "00:00:00.0015505",
"timestamp": "2026-01-14T17:55:39.7914455Z",
"checks": [
{
"name": "PostgreSQL",
"status": "Healthy",
"description": "PostgreSQL database connection is healthy",
"duration": "00:00:00.0014398",
"tags": [
"database",
"sql"
],
"data": {
"DatabaseName": "MilvaionDb",
"ConnectionStatus": "Connected",
"ProviderName": "Npgsql.EntityFrameworkCore.PostgreSQL"
}
},
{
"name": "Redis",
"status": "Healthy",
"description": "Redis connection is healthy",
"duration": "00:00:00.0004801",
"tags": [
"redis",
"cache"
],
"data": {
"ConnectionStatus": "Connected",
"Database": "0"
}
},
{
"name": "RabbitMQ",
"status": "Healthy",
"description": "RabbitMQ connection is healthy",
"duration": "00:00:00.0000037",
"tags": [
"rabbitmq",
"messaging"
],
"data": {
"ConnectionStatus": "Connected",
"Host": "rabbitmq",
"Port": "5672",
"IsOpen": "True"
}
}
]
}
Kubernetes Probes
spec:
containers:
- name: api
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/v1/healthcheck/live
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 3
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/v1/healthcheck/ready
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 3
Worker Health
Workers support two health check approaches: file-based (for Console Workers) and HTTP endpoint-based (for API Workers).
Configuration
Enable health checks in appsettings.json:
{
"Worker": {
"HealthCheck": {
"Enabled": true,
"LiveFilePath": "/tmp/live", // Only for file health check. (for console workers)
"ReadyFilePath": "/tmp/ready", // Only for file health check. (for console workers)
"IntervalSeconds": 30
}
}
}
| Setting | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
Enabled | false | Enable/disable health checks |
LiveFilePath | /tmp/live | File path for liveness probe |
ReadyFilePath | /tmp/ready | File path for readiness probe |
IntervalSeconds | 30 | Health check interval |
Option 1: Console Worker (File-Based)
For workers without HTTP endpoints, use AddFileHealthCheck():
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Milvasoft.Milvaion.Sdk.Worker;
var builder = Host.CreateApplicationBuilder(args);
// Register Worker SDK
builder.Services.AddMilvaionWorkerWithJobs(builder.Configuration);
// Add file-based health checks (Redis + RabbitMQ)
builder.Services.AddFileHealthCheck(builder.Configuration);
var host = builder.Build();
await host.RunAsync();
Kubernetes probes:
spec:
containers:
- name: worker
livenessProbe:
exec:
command: ["test", "-f", "/tmp/live"]
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 30
failureThreshold: 3
readinessProbe:
exec:
command: ["test", "-f", "/tmp/ready"]
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 3
Docker Compose healthcheck:
worker:
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "test", "-f", "/tmp/live"]
interval: 30s
timeout: 5s
retries: 3
start_period: 30s
Option 2: API Worker (HTTP Endpoints)
For workers with HTTP endpoints, use AddHealthCheckEndpoints() and UseHealthCheckEndpoints():
using Milvasoft.Milvaion.Sdk.Worker;
using Milvasoft.Milvaion.Sdk.Worker.HealthChecks;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add health checks (Redis + RabbitMQ)
builder.Services.AddHealthChecks()
.AddCheck<RedisHealthCheck>("Redis", tags: ["redis", "cache"])
.AddCheck<RabbitMQHealthCheck>("RabbitMQ", tags: ["rabbitmq", "messaging"]);
// Register Worker SDK
builder.Services.AddMilvaionWorkerWithJobs(builder.Configuration);
// Register health check endpoint services
builder.Services.AddHealthCheckEndpoints(builder.Configuration);
var app = builder.Build();
// Map health check endpoints
app.UseHealthCheckEndpoints(builder.Configuration);
await app.RunAsync();
Available endpoints:
| Endpoint | Purpose | Response |
|---|---|---|
/health | Simple check | "Ok" |
/health/live | Liveness probe | { status, timestamp, uptime } |
/health/ready | Readiness probe | { status, duration, checks[] } |
/health/startup | Startup probe | { status, timestamp, uptime } |
Kubernetes probes:
spec:
containers:
- name: api-worker
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health/live
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
failureThreshold: 3
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health/ready
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 3
startupProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health/startup
port: 8080
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 30
Health Check Behavior
The SDK includes built-in health checks for:
| Check | What it Verifies |
|---|---|
| Redis | Connection status via PING command |
| RabbitMQ | Connection status via IConnectionMonitor |
File-based health check logic:
- Live file exists: Worker process is running and not completely unhealthy
- Ready file exists: All health checks (Redis, RabbitMQ) are healthy
- Files are deleted on graceful shutdown
- Files are updated every
IntervalSeconds
Dashboard Metrics
Built-in Statistics
Access via Dashboard home or API:
curl http://localhost:5000/api/v1/dashboard
{
"isSuccess": true,
"statusCode": 200,
"messages": [
{
"key": "",
"message": "Operation successful!",
"type": 1
}
],
"data": {
"totalExecutions": 3546,
"queuedJobs": 0,
"completedJobs": 3513,
"failedOccurrences": 32,
"cancelledJobs": 1,
"timedOutJobs": 0,
"runningJobs": 0,
"averageDuration": 2509.362653003131,
"successRate": 99.06937394247038,
"totalWorkers": 1,
"totalWorkerInstances": 1,
"workerCurrentJobs": 0,
"workerMaxCapacity": 128,
"workerUtilization": 0,
"executionsPerMinute": 10,
"executionsPerSecond": 0, // It means lower than 1
"peakExecutionsPerMinute": 10
},
"metadatas": []
}
Worker Status
curl http://localhost:5000/api/v1/workers
[
{
"isSuccess": true,
"statusCode": 200,
"messages": [],
"data": [
{
"workerId": "sample-worker",
"displayName": "sample-worker (sample-worker-172a5243)",
"routingPatterns": {
"AlwaysFailingJob": "alwaysfailing.*",
"LongRunningTestJob": "longrunningtest.*",
"NonParallelJob": "nonparallel.*",
"SendEmailJob": "sendemail.*",
"TestJob": "test.*"
},
"jobNames": [
"AlwaysFailingJob",
"LongRunningTestJob",
"NonParallelJob",
"SendEmailJob",
"TestJob"
],
"currentJobs": 0,
"status": "Active",
"lastHeartbeat": "2026-01-14T18:04:52.0539333+00:00",
"registeredAt": "2026-01-14T18:01:27.1426831+00:00",
"version": "1.0.0.0",
"metadata": "{\"ProcessorCount\":16,\"OSVersion\":\"Unix 6.6.87.1\",\"RuntimeVersion\":\"10.0.1\",\"JobConfigs\":[{\"JobType\":\"AlwaysFailingJob\",\"ConsumerId\":\"alwaysfailing-consumer\",\"MaxParallelJobs\":8,\"ExecutionTimeoutSeconds\":30},{\"JobType\":\"LongRunningTestJob\",\"ConsumerId\":\"longrunning-consumer\",\"MaxParallelJobs\":8,\"ExecutionTimeoutSeconds\":10},{\"JobType\":\"NonParallelJob\",\"ConsumerId\":\"nonparallel-consumer\",\"MaxParallelJobs\":1,\"ExecutionTimeoutSeconds\":30},{\"JobType\":\"SendEmailJob\",\"ConsumerId\":\"email-consumer\",\"MaxParallelJobs\":16,\"ExecutionTimeoutSeconds\":600},{\"JobType\":\"TestJob\",\"ConsumerId\":\"test-consumer\",\"MaxParallelJobs\":32,\"ExecutionTimeoutSeconds\":120}]}",
"instances": [
{
"instanceId": "sample-worker-172a5243",
"hostName": "1fc7768572fd",
"ipAddress": "172.18.0.6",
"currentJobs": 0,
"status": 0,
"lastHeartbeat": "2026-01-14T18:04:52.0539333+00:00",
"registeredAt": "2026-01-14T18:01:27.1454977+00:00"
}
]
}
],
"metadatas": []
}
]
Logging
Milvaion uses Serilog for structured logging. By default, logs are written to the console. You can optionally enable Seq integration for centralized log management.
Default Behavior
- Console output: All logs are written to console by default
- Structured format: Logs include contextual properties for filtering
- Automatic enrichment: Each log entry includes
AppNameandEnvironmentproperties - Path filtering: Health check and metrics endpoints are excluded from logs
Seq Integration (Optional)
To send logs to Seq, enable it in appsettings.json:
{
"MilvaionConfig": {
"Logging": {
"Seq": {
"Enabled": true,
"Uri": "http://seq:5341"
}
}
}
}
| Setting | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
Enabled | false | Enable/disable Seq logging |
Uri | - | Seq server URL |
Log Level Configuration
Configure log levels via the standard Serilog configuration:
{
"Serilog": {
"MinimumLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Override": {
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Information",
"System": "Warning",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc": "Warning",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Cors": "Warning",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Routing": "Warning",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting.Diagnostics": "Warning",
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command": "Warning",
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Update": "Warning",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer.JwtBearerHandler": "Warning"
}
}
}
}
| Level | Use For |
|---|---|
Verbose | Detailed debugging (very noisy) |
Debug | Development diagnostics |
Information | General operational events |
Warning | Unexpected but handled events |
Error | Failures requiring attention |
Fatal | Critical failures |
Log Enrichment
All log entries are automatically enriched with:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
AppName | Application identifier (milvaion-api) |
Environment | Current deployment environment (MILVA_ENV environment variable) |
Log Correlation
Use CorrelationId to trace a job across services. In Seq:
CorrelationId = "corr-789"
OpenTelemetry Integration
Milvaion includes built-in OpenTelemetry support for metrics and distributed tracing. Metrics are exposed via a Prometheus-compatible HTTP endpoint.
Configuration
Enable and configure OpenTelemetry in appsettings.json:
{
"MilvaionConfig": {
"OpenTelemetry": {
"Enabled": true,
"ExportPath": "/api/metrics",
"Service": "milvaion-api",
"Environment": "production",
"Job": "api",
"Instance": "milvaion-prod-01"
}
}
}
| Setting | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
Enabled | false | Enable/disable OpenTelemetry observability |
ExportPath | /api/metrics | Prometheus scraping endpoint path |
Service | milvaion-api | Service name for resource identification |
Environment | MILVA_ENV env var | Environment label (e.g., production, staging) |
Job | api | Job label for Prometheus |
Instance | Machine name | Instance identifier for multi-instance deployments |
Accessing Metrics
Prometheus metrics are exposed at the configured ExportPath:
curl http://localhost:5000/api/metrics
This endpoint returns metrics in Prometheus text format, ready for scraping.
Collected Metrics
The following metric sources are automatically instrumented:
| Source | Description |
|---|---|
| ASP.NET Core | HTTP request duration, status codes, active requests |
| HTTP Client | Outbound HTTP request metrics |
| Process | CPU, memory, GC, thread pool metrics |
| Npgsql (PostgreSQL) | Database query metrics |
| Entity Framework Core | ORM-level database metrics |
| System.Net.Http | HTTP client diagnostics |
| System.Net.NameResolution | DNS resolution metrics |
| System.Threading | Thread pool and synchronization metrics |
| System.Runtime | .NET runtime metrics |
Background Service Metrics
Milvaion exposes custom metrics for all background services via the Milvaion.BackgroundServices meter:
Job Dispatcher:
| Metric | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
milvaion_dispatcher_jobs_dispatched | Counter | Total jobs dispatched to workers |
milvaion_dispatcher_dispatch_failures | Counter | Total dispatch failures |
milvaion_dispatcher_dispatch_duration | Histogram | Duration of dispatch operations (ms) |
milvaion_dispatcher_pending_jobs | Gauge | Jobs pending dispatch |
Status Tracker:
| Metric | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
milvaion_status_tracker_updates_processed | Counter | Total status updates processed |
milvaion_status_tracker_update_failures | Counter | Total status update failures |
milvaion_status_tracker_batch_duration | Histogram | Batch processing duration (ms) |
milvaion_status_tracker_updates_by_status | Counter | Updates by final status (labels: status) |
milvaion_status_tracker_batch_size | Gauge | Current batch size |
Log Collector:
| Metric | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
milvaion_log_collector_logs_collected | Counter | Total worker logs collected |
milvaion_log_collector_collection_failures | Counter | Total collection failures |
milvaion_log_collector_batch_duration | Histogram | Log batch processing duration (ms) |
milvaion_log_collector_batch_size | Gauge | Current log batch size |
Worker Discovery:
| Metric | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
milvaion_worker_discovery_registrations | Counter | Total worker registrations |
milvaion_worker_discovery_heartbeats | Counter | Total heartbeats received |
milvaion_worker_discovery_heartbeat_failures | Counter | Heartbeat processing failures |
milvaion_worker_discovery_heartbeat_duration | Histogram | Heartbeat batch processing duration (ms) |
milvaion_worker_discovery_active_workers | Gauge | Currently active workers |
Zombie Detector:
| Metric | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
milvaion_zombie_detector_detected | Counter | Zombie occurrences detected |
milvaion_zombie_detector_recovered | Counter | Zombie occurrences recovered |
milvaion_zombie_detector_detection_duration | Histogram | Detection scan duration (ms) |
Failed Occurrence Handler:
| Metric | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
milvaion_failed_handler_processed | Counter | Failed occurrences processed |
milvaion_failed_handler_retried | Counter | Failed occurrences retried |
milvaion_failed_handler_process_duration | Histogram | Processing duration (ms) |
General Service Metrics:
| Metric | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
milvaion_background_service_iterations | Counter | Service loop iterations (labels: service) |
milvaion_background_service_errors | Counter | Service errors (labels: service, error_type) |
milvaion_background_service_iteration_duration | Histogram | Iteration duration (labels: service) |
Distributed Tracing
Tracing is automatically configured for:
- ASP.NET Core requests (with exception recording)
- HTTP client calls
- PostgreSQL queries (via Npgsql)
- Entity Framework Core operations
- Milvaion internal activity sources
Trace data includes resource attributes for correlation:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
service | Service name |
environment | Deployment environment |
job | Job identifier |
instance | Instance identifier |
Prometheus Scrape Configuration
Add Milvaion to your Prometheus configuration:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'milvaion-api'
scrape_interval: 15s
static_configs:
- targets: ['milvaion-api:5000']
metrics_path: '/api/metrics'
Alerting
Critical Alerts
| Condition | Severity | Action |
|---|---|---|
| API health check failing | Critical | Page on-call |
| All workers offline | Critical | Page on-call |
| DLQ depth > 100 | High | Investigate failures |
| Success rate < 95% | High | Check failing jobs |
| Queue depth growing | Medium | Scale workers |
| Zombie jobs detected | Medium | Check worker health |
Prometheus Alert Rules
groups:
- name: milvaion
rules:
- alert: MilvaionApiDown
expr: up{job="milvaion-api"} == 0
for: 1m
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: "Milvaion API is down"
- alert: MilvaionNoActiveWorkers
expr: count(milvaion_worker_active) == 0
for: 2m
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: "No active Milvaion workers"
- alert: MilvaionHighFailureRate
expr: |
rate(milvaion_jobs_failed[5m]) /
rate(milvaion_jobs_completed[5m]) > 0.1
for: 5m
labels:
severity: high
annotations:
summary: "Job failure rate > 10%"
- alert: MilvaionDLQGrowing
expr: milvaion_dlq_depth > 50
for: 10m
labels:
severity: high
annotations:
summary: "Dead letter queue has {{ $value }} messages"
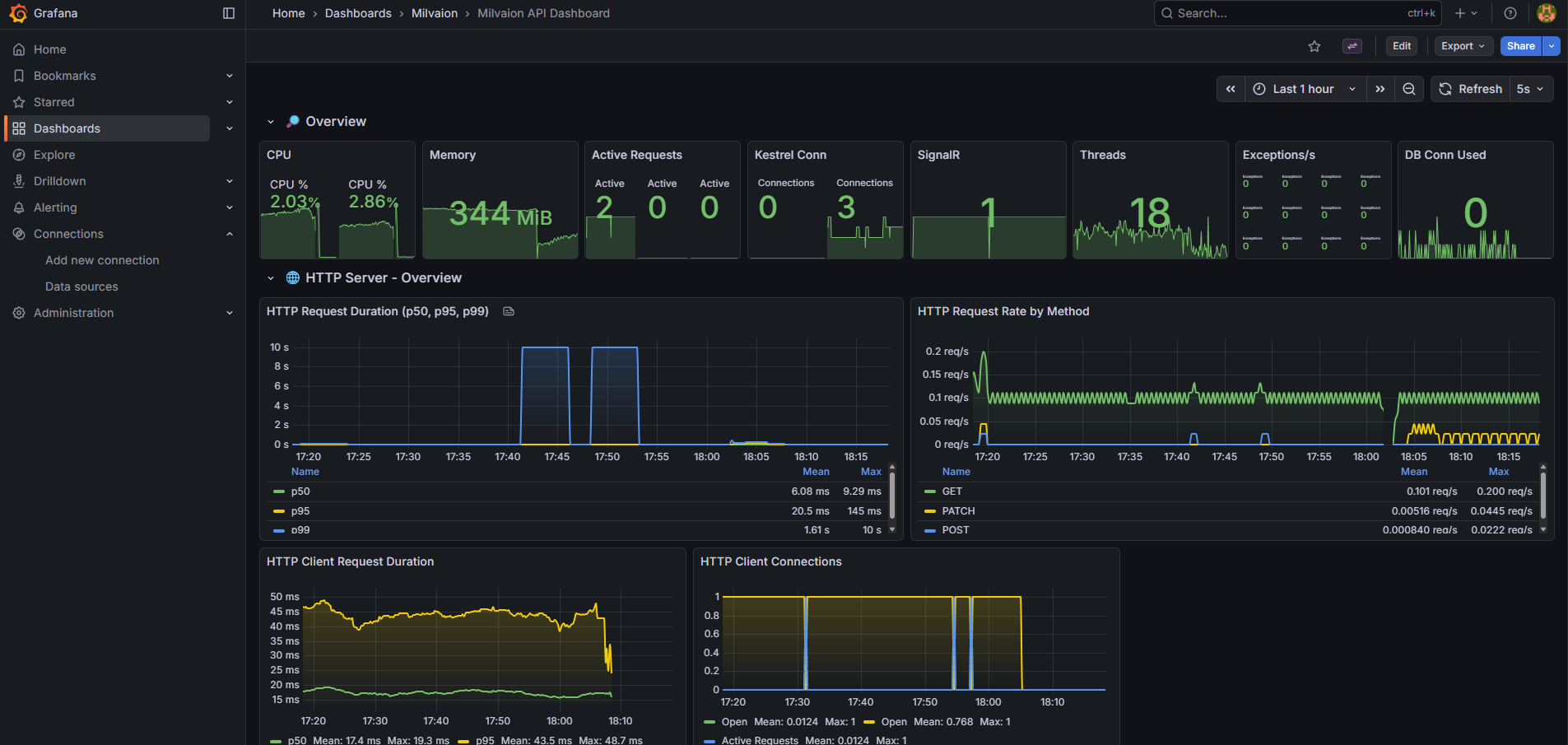
Grafana Dashboards
Milvaion includes two pre-configured Grafana dashboards located in build/grafana/provisioning/dashboards/json/:
1. Milvaion API Dashboard (milvaion-api.json)
General API and infrastructure monitoring:
| Section | Panels |
|---|---|
| Overview | CPU, Memory, Active Requests, Kestrel Connections, SignalR, Thread Pool |
| HTTP Requests | Request Rate, Response Times (p50/p95/p99), Status Codes, Error Rate |
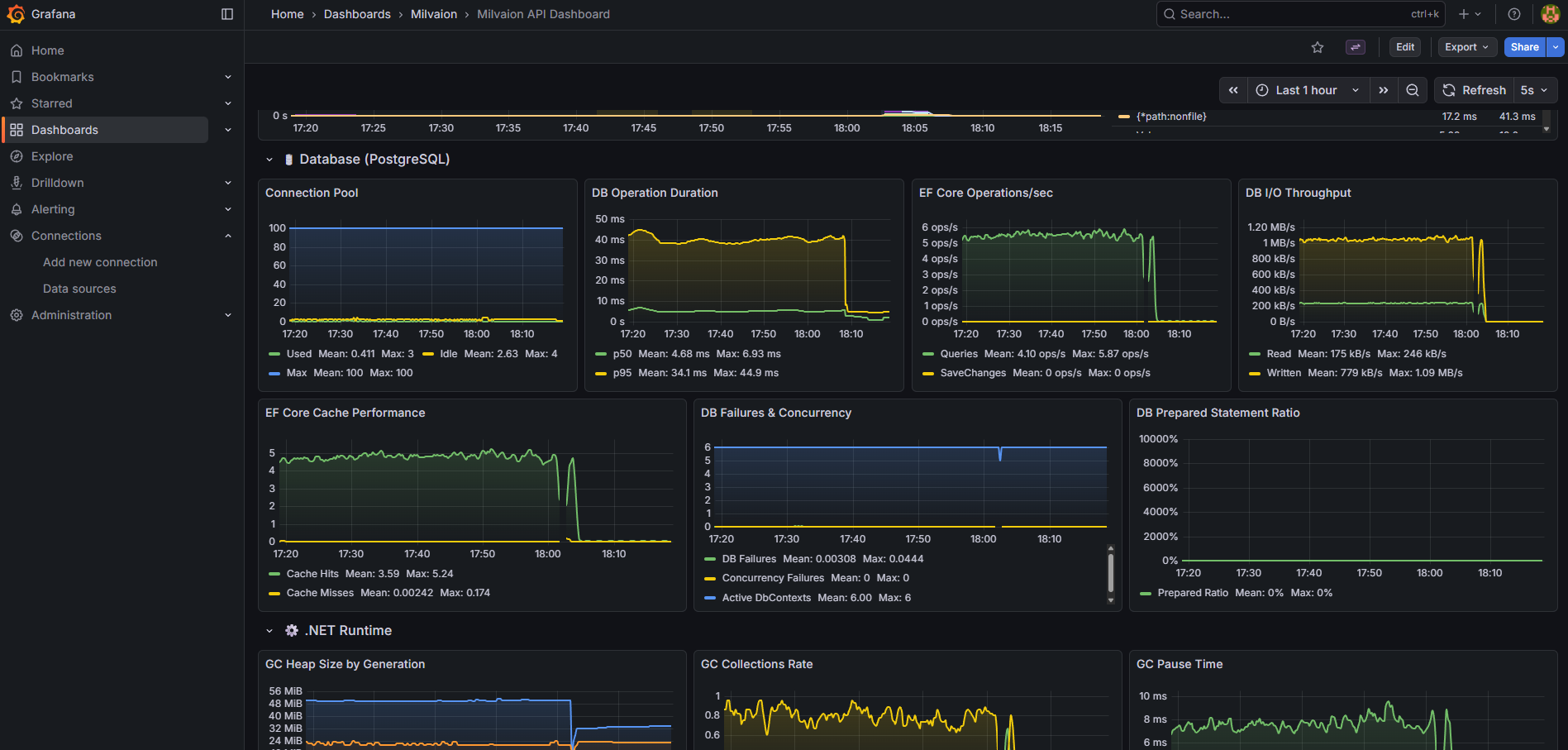
| Database | Query Duration, Active Connections, Commands/sec, Connection Pool |
| Memory | GC Collections, Heap Size, LOH Size, Allocation Rate |
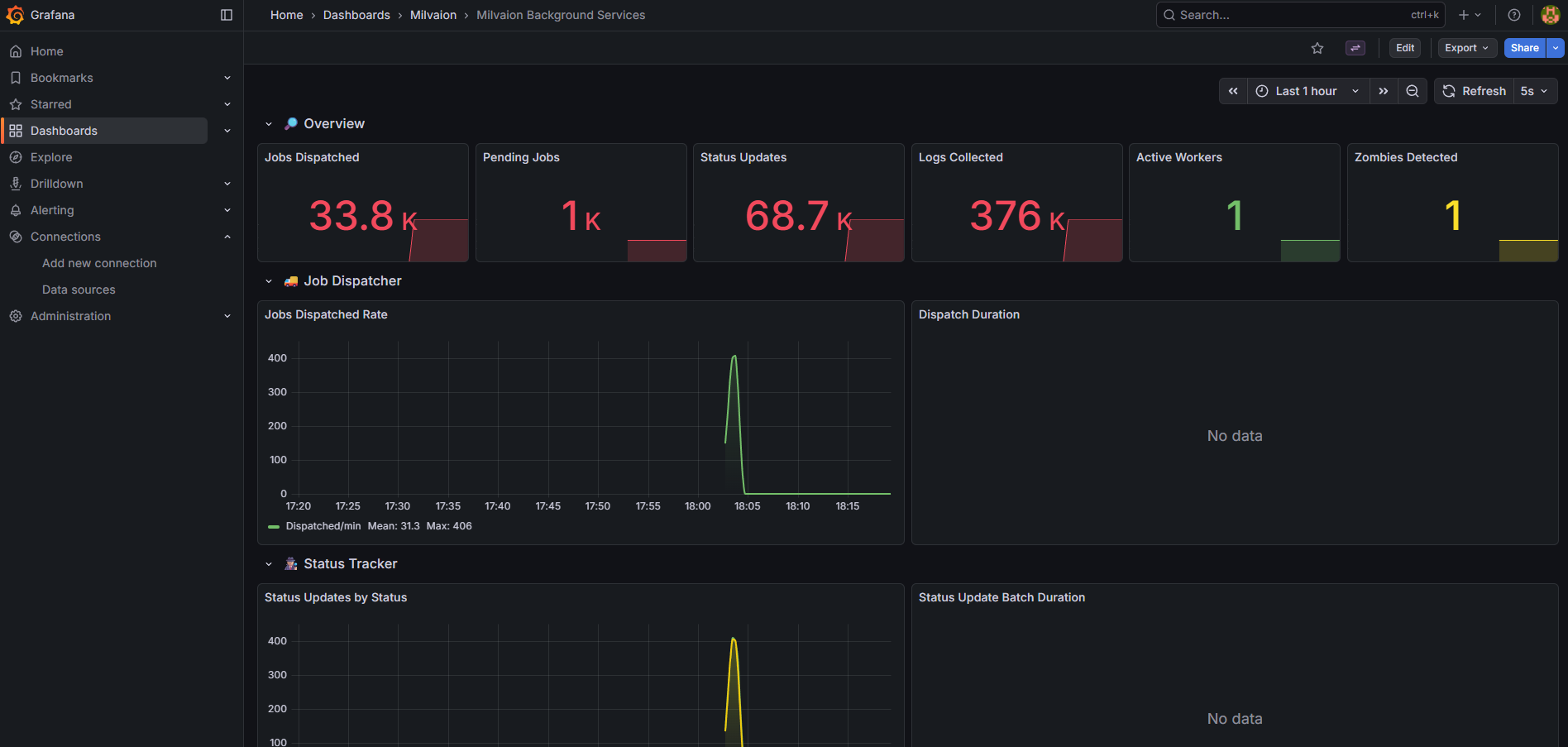
2. Background Services Dashboard (milvaion-background-services.json)
Dedicated monitoring for all background services:
| Section | Panels |
|---|---|
| Overview | Jobs Dispatched, Pending Jobs, Status Updates, Logs Collected, Active Workers, Zombies Detected |
| Job Dispatcher | Dispatch Rate (jobs/min), Dispatch Duration (p50/p95/p99), Failures |
| Status Tracker | Updates by Status, Batch Duration, Failures |
| Log Collector | Collection Rate, Batch Duration, Queue Size |
| Worker Discovery | Registrations/min, Heartbeats/min, Active Workers, Heartbeat Duration |
| Zombie & Failed Handlers | Zombies Detected/Recovered, Failed Occurrences Processed/Retried |
| Service Health | Errors by Service, Iteration Duration by Service |
Useful PromQL Queries
# Jobs dispatched per minute
rate(milvaion_dispatcher_jobs_dispatched_total{job="milvaion-api"}[1m]) * 60
# Dispatch failure rate
rate(milvaion_dispatcher_dispatch_failures_total[5m]) / rate(milvaion_dispatcher_jobs_dispatched_total[5m])
# Status updates by status type
sum by (status) (rate(milvaion_status_tracker_updates_by_status_total[5m]))
# Average dispatch duration (p95)
histogram_quantile(0.95, sum(rate(milvaion_dispatcher_dispatch_duration_bucket[5m])) by (le))
# Active workers count
milvaion_worker_discovery_active_workers
# Zombie detection rate (per 5 minutes)
increase(milvaion_zombie_detector_detected_total[5m])
# Service error rate by service
sum by (service) (rate(milvaion_background_service_errors_total[5m]))
Access Dashboards
- Grafana UI: http://localhost:3000 (default: admin/admin)
- Milvaion API Dashboard: Pre-loaded as "Milvaion API Dashboard"
- Background Services Dashboard: Pre-loaded as "Milvaion Background Services"
RabbitMQ Monitoring
Management UI
Access at http://localhost:15672:
- Overview: Message rates, connections
- Queues: Depth, consumers, message rates
- Exchanges: Routing statistics
Key Metrics
| Metric | Healthy Range | Action if Exceeded |
|---|---|---|
| Queue depth | < 1000 | Scale workers |
| Unacked messages | < 100 | Check worker health |
| Memory usage | < 80% | Add RAM or scale |
| Disk alarm | Not triggered | Add disk space |
CLI Monitoring
# Queue status
docker exec milvaion-rabbitmq rabbitmqctl list_queues name messages consumers
# Connection count
docker exec milvaion-rabbitmq rabbitmqctl list_connections
Redis Monitoring
Key Metrics
| Metric | Command | Healthy Range |
|---|---|---|
| Memory used | INFO memory | < 80% maxmemory |
| Connected clients | INFO clients | < 10000 |
| Commands/sec | INFO stats | Varies |
| Keyspace | INFO keyspace | Growing slowly |
CLI Commands
# Memory info
docker exec milvaion-redis redis-cli INFO memory
# Slow queries
docker exec milvaion-redis redis-cli SLOWLOG GET 10
# Active keys
docker exec milvaion-redis redis-cli DBSIZE
Database Monitoring
PostgreSQL Key Metrics
| Metric | Query | Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Active connections | SELECT count(*) FROM pg_stat_activity | < max_connections |
| Long-running queries | SELECT * FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE state = 'active' AND query_start < now() - interval '5 minutes' | 0 |
| Table bloat | SELECT pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size('JobOccurrences')) | Monitor growth |
Useful Queries
-- Occurrence count by status (last 24h)
SELECT "Status", COUNT(*)
FROM "JobOccurrences"
WHERE "CreatedAt" > NOW() - INTERVAL '24 hours'
GROUP BY "Status";
-- Slowest jobs (avg duration)
SELECT j."JobType", AVG(o."DurationMs") as avg_ms, COUNT(*) as count
FROM "JobOccurrences" o
JOIN "ScheduledJobs" j ON o."JobId" = j."Id"
WHERE o."Status" = 2 -- Completed
GROUP BY j."JobType"
ORDER BY avg_ms DESC
LIMIT 10;
-- Failed jobs by type (last 7 days)
SELECT j."JobType", COUNT(*) as failures
FROM "JobOccurrences" o
JOIN "ScheduledJobs" j ON o."JobId" = j."Id"
WHERE o."Status" = 3 -- Failed
AND o."CreatedAt" > NOW() - INTERVAL '7 days'
GROUP BY j."JobType"
ORDER BY failures DESC;
Troubleshooting
Jobs Not Executing
- Check dispatcher is running:
docker logs milvaion-api | grep -i dispatch - Check workers are registered:
curl http://localhost:5000/api/v1/workers - Check RabbitMQ queues: http://localhost:15672
- Check Redis scheduled jobs:
docker exec milvaion-redis redis-cli ZRANGE "Milvaion:JobScheduler:scheduled_jobs" 0 -1 WITHSCORES
High Memory Usage
- Check for large job payloads
- Check occurrence log sizes
- Enable database cleanup jobs
- Check for memory leaks in custom jobs
Slow Dashboard
- Check PostgreSQL query performance
- Add indexes if missing
- Increase API connection pool
- Enable response caching
What's Next?
- Database Maintenance - Cleanup and retention policies
- Security – Security considerations
- MilvaionUI – UI screenshoots